How much Interior Forest is enough?

The 2018 Muskoka Watershed Report Card produced by the Muskoka Watershed Council features 8 different indicators of watershed health. Interior Forest is one of these indicators, categorized as a health indicator rather than a threat indicator as it contributes to the health of our watershed.
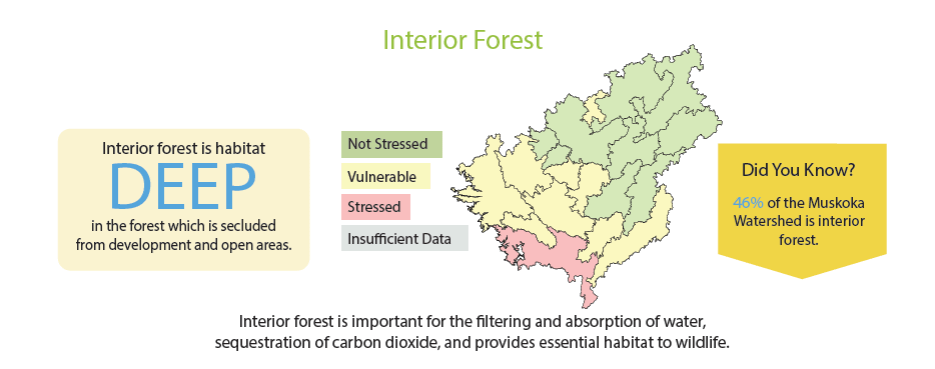
Interior forest habitat is located deep in the forest, secluded from the impacts of forest edge development and open habitats. The interior forest in Muskoka is primarily comprised of shade-tolerant and late-successional species such as sugar maple, American beech, basswood, ironwood, hemlock, and eastern white cedar. A group of mid-tolerant shade tree species such as eastern white pine, red pine, red oak, bur oak, swamp white oak, ash, yellow birch and black cherry are less common, but still important in interior forest in Muskoka.
Many of Muskoka’s wildlife species depend on interior forest habitat, however the development of roads, houses and other human-made structures fragment forested land, greatly reducing the amount of interior forest. Interior forest ecosystems can be threatened by permanent changes to the landscape such as development and permanent roads, however smaller impacts may also arise from less intensively used seasonal trails like snowmobile trails.
Although fragmented forests can still provide habitat for a vast array of wildlife, they lack patches of interior forest of sufficient size to sustain many interior species. Fragmentation can also interrupt the ecologically important connectivity across forested land.
Ecosystem functions provided by interior forests include the filtering and absorption of water into the ground; absorption of large amounts of carbon dioxide that would otherwise be released into the atmosphere; and photosynthesis. These ecological services and more are essential to wildlife well-being, as well as human health.
The 2018 Muskoka Watershed Report Card reports on the amount of Interior Forest in each quaternary watershed. Currently, the total interior forest cover across the Muskoka Watershed is 46%, but the amount of interior forest habitat in each quaternary watershed varies greatly across Muskoka, from approximately 17% in the Severn River Watershed to over 60% in the Rosseau River Watershed. More than 50% of a quaternary watershed should be comprised of interior forest in order for it to be considered not stressed.
How much interior forest is in your watershed? Check out the 2018 Muskoka Watershed Report Card at https://muskokawatershed.org to find out.